Package tomotopy
Python package tomotopy provides types and functions for various Topic Model
including LDA, DMR, HDP, MG-LDA, PA and HPA. It is written in C++ for speed and provides Python extension.
What is tomotopy?
tomotopy is a Python extension of tomoto (Topic Modeling Tool) which is a Gibbs-sampling based topic model library written in C++.
It utilizes a vectorization of modern CPUs for maximizing speed.
The current version of tomoto supports several major topic models including
- Latent Dirichlet Allocation (
LDAModel) - Labeled LDA (
LLDAModel) - Partially Labeled LDA (
PLDAModel) - Supervised LDA (
SLDAModel) - Dirichlet Multinomial Regression (
DMRModel) - Hierarchical Dirichlet Process (
HDPModel) - Hierarchical LDA (
HLDAModel) - Multi Grain LDA (
MGLDAModel) - Pachinko Allocation (
PAModel) - Hierarchical PA (
HPAModel) - Correlated Topic Model (
CTModel) - Dynamic Topic Model (
DTModel).
The most recent version of tomotopy is 0.7.0.
Getting Started
You can install tomotopy easily using pip. (https://pypi.org/project/tomotopy/) ::
$ pip install tomotopy
The supported OS and Python versions are:
- Linux (x86-64) with Python >= 3.5
- macOS >= 10.13 with Python >= 3.5
- Windows 7 or later (x86, x86-64) with Python >= 3.5
- Other OS with Python >= 3.5: Compilation from source code required (with c++11 compatible compiler)
After installing, you can start tomotopy by just importing. ::
import tomotopy as tp
print(tp.isa) # prints 'avx2', 'avx', 'sse2' or 'none'
Currently, tomotopy can exploits AVX2, AVX or SSE2 SIMD instruction set for maximizing performance.
When the package is imported, it will check available instruction sets and select the best option.
If tp.isa tells none, iterations of training may take a long time.
But, since most of modern Intel or AMD CPUs provide SIMD instruction set, the SIMD acceleration could show a big improvement.
Here is a sample code for simple LDA training of texts from 'sample.txt' file. ::
import tomotopy as tp
mdl = tp.LDAModel(k=20)
for line in open('sample.txt'):
mdl.add_doc(line.strip().split())
for i in range(0, 100, 10):
mdl.train(10)
print('Iteration: {}\tLog-likelihood: {}'.format(i, mdl.ll_per_word))
for k in range(mdl.k):
print('Top 10 words of topic #{}'.format(k))
print(mdl.get_topic_words(k, top_n=10))
Performance Of Tomotopy
tomotopy uses Collapsed Gibbs-Sampling(CGS) to infer the distribution of topics and the distribution of words.
Generally CGS converges more slowly than Variational Bayes(VB) that gensim's LdaModel uses, but its iteration can be computed much faster.
In addition, tomotopy can take advantage of multicore CPUs with a SIMD instruction set, which can result in faster iterations.
Following chart shows the comparison of LDA model's running time between tomotopy and gensim.
The input data consists of 1000 random documents from English Wikipedia with 1,506,966 words (about 10.1 MB).
tomotopy trains 200 iterations and gensim trains 10 iterations.
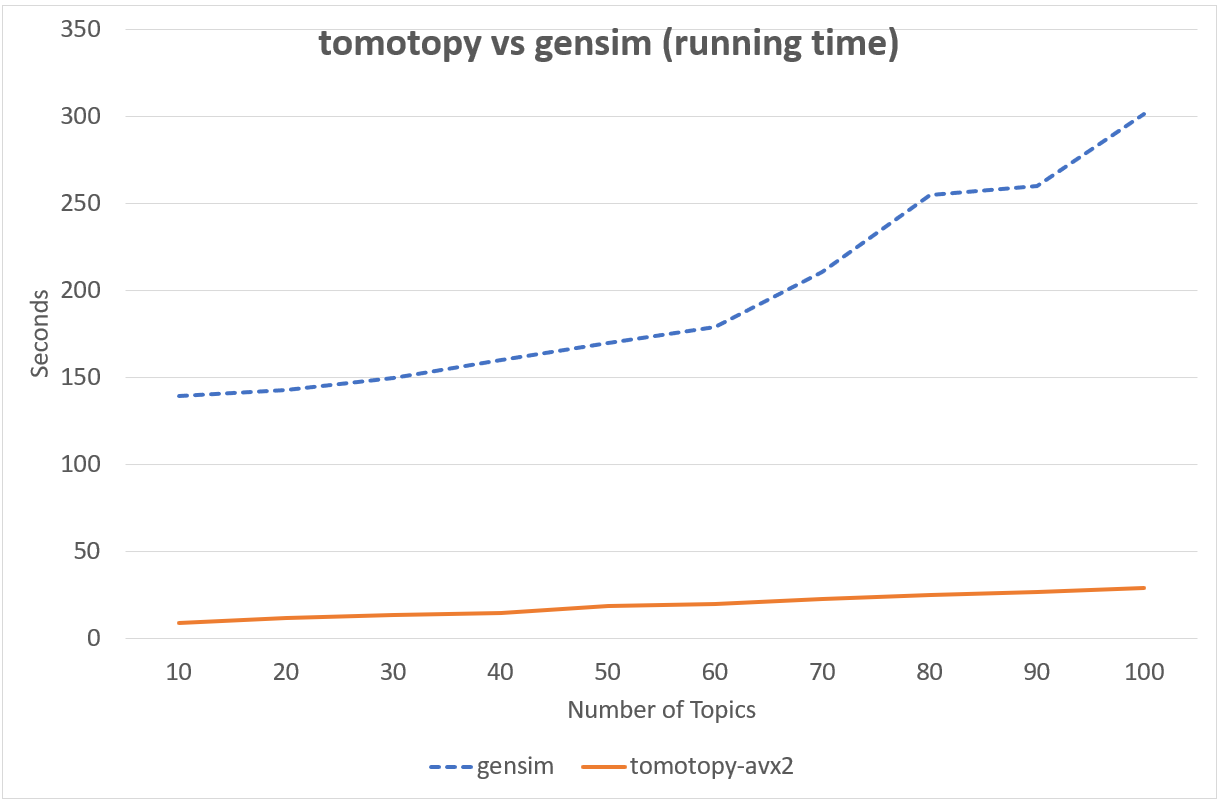
↑ Performance in Intel i5-6600, x86-64 (4 cores)
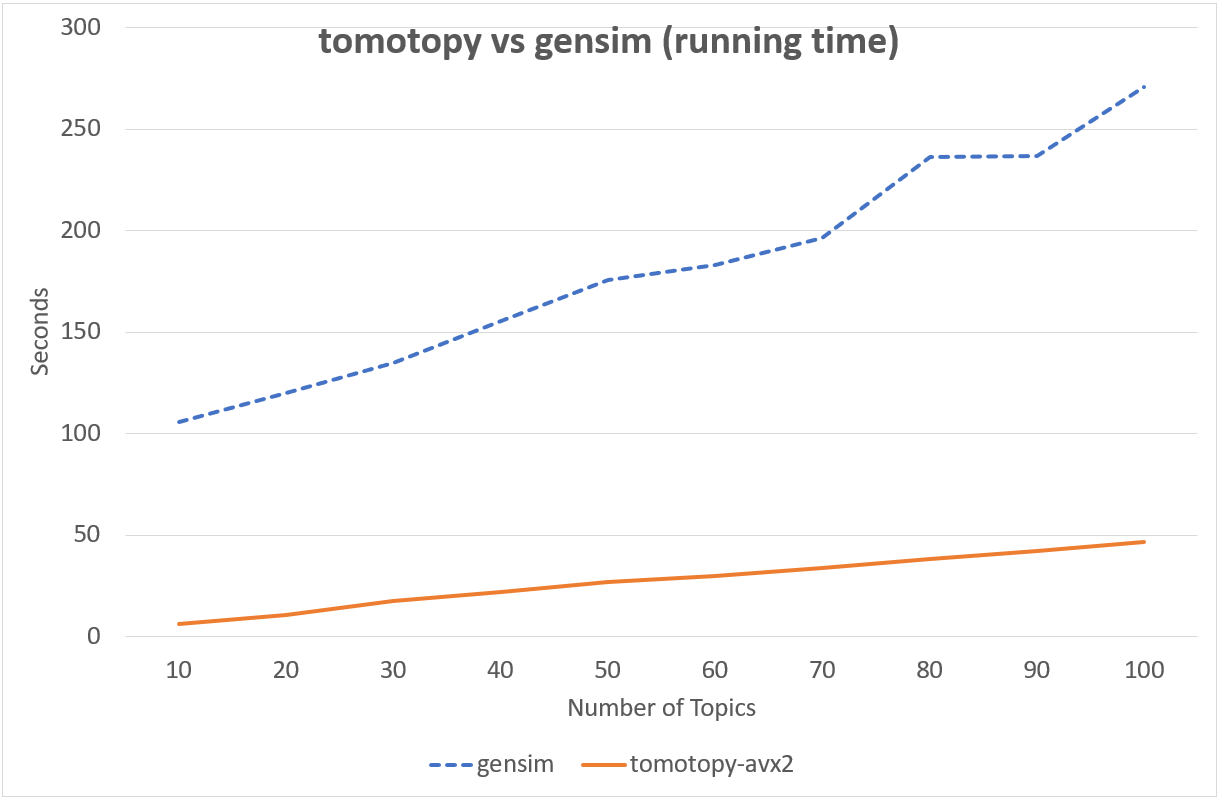
↑ Performance in Intel Xeon E5-2620 v4, x86-64 (8 cores, 16 threads)
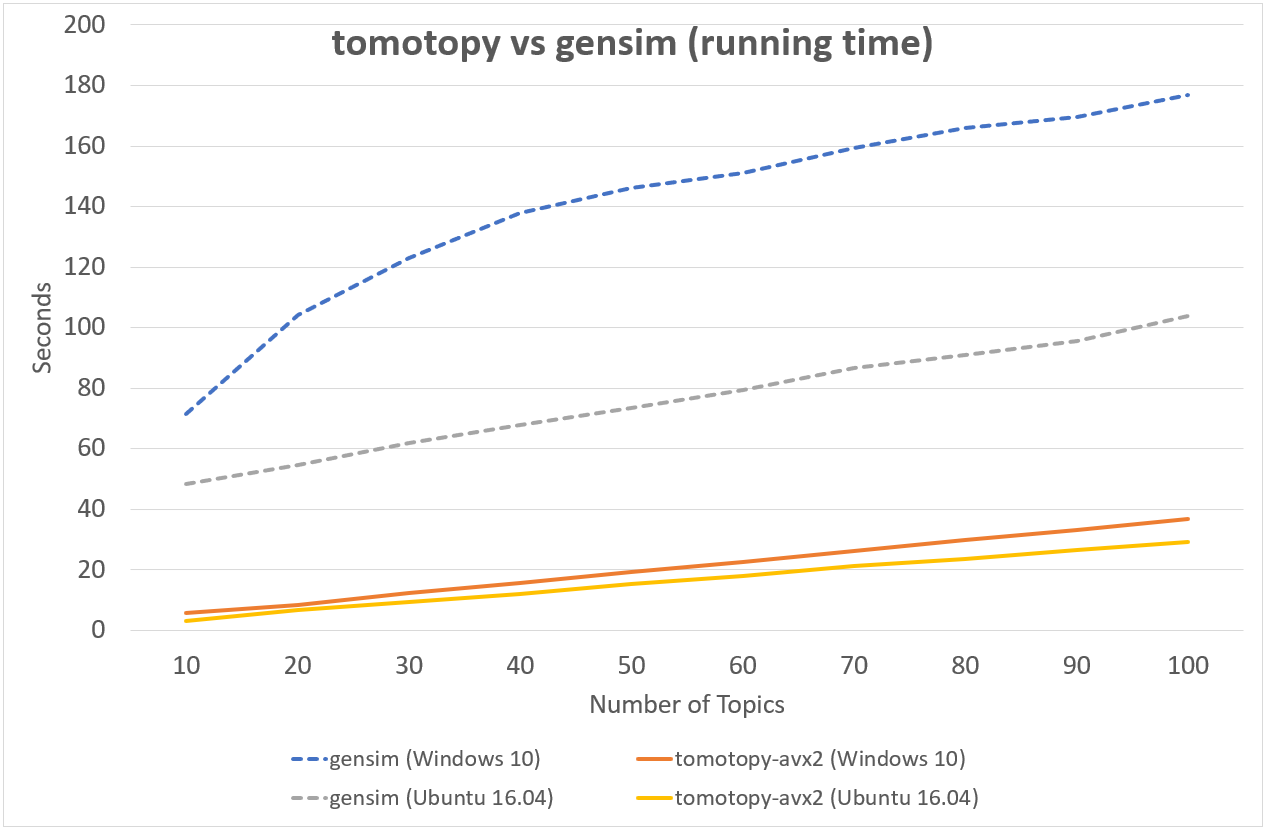
↑ Performance in AMD Ryzen7 3700X, x86-64 (8 cores, 16 threads)
Although tomotopy iterated 20 times more, the overall running time was 5~10 times faster than gensim. And it yields a stable result.
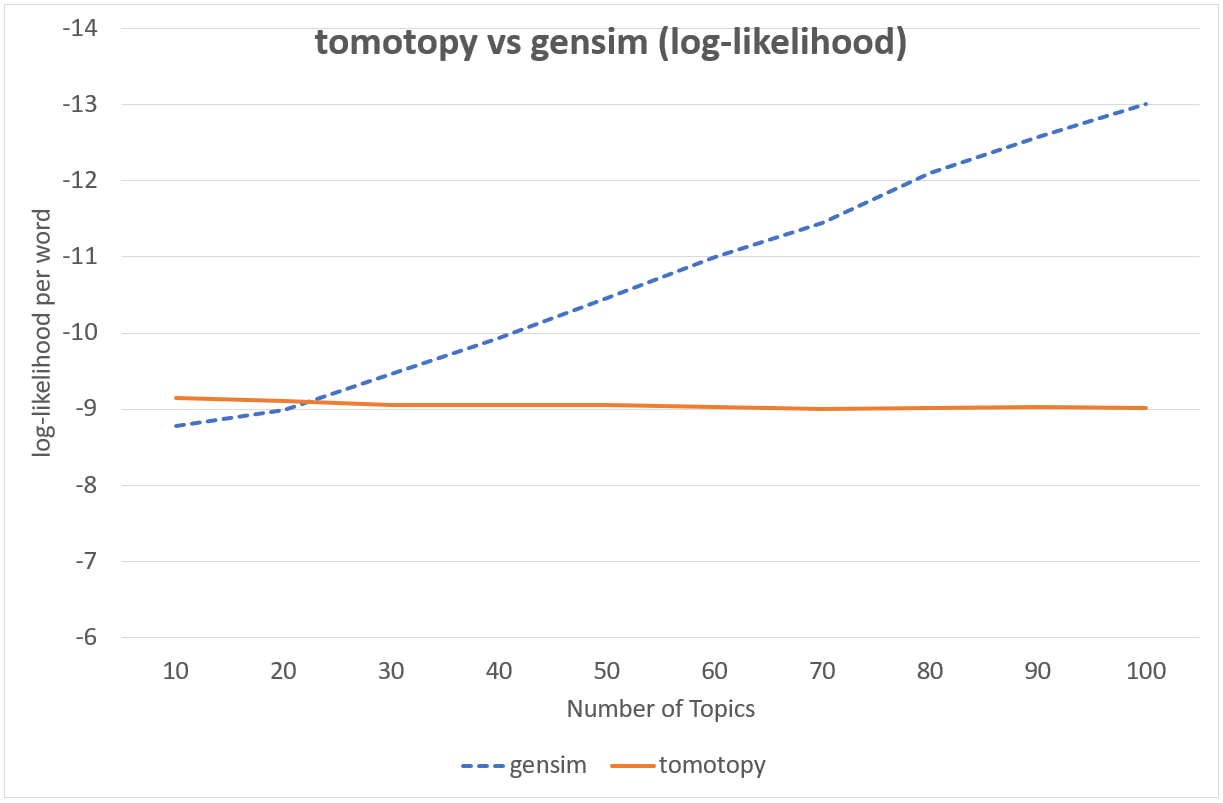
It is difficult to compare CGS and VB directly because they are totaly different techniques. But from a practical point of view, we can compare the speed and the result between them. The following chart shows the log-likelihood per word of two models' result.
Top words of topics generated by tomotopy | |
|---|---|
| #1 | use, acid, cell, form, also, effect |
| #2 | use, number, one, set, comput, function |
| #3 | state, use, may, court, law, person |
| #4 | state, american, nation, parti, new, elect |
| #5 | film, music, play, song, anim, album |
| #6 | art, work, design, de, build, artist |
| #7 | american, player, english, politician, footbal, author |
| #8 | appl, use, comput, system, softwar, compani |
| #9 | day, unit, de, state, german, dutch |
| #10 | team, game, first, club, leagu, play |
| #11 | church, roman, god, greek, centuri, bc |
| #12 | atom, use, star, electron, metal, element |
| #13 | alexand, king, ii, emperor, son, iii |
| #14 | languag, arab, use, word, english, form |
| #15 | speci, island, plant, famili, order, use |
| #16 | work, univers, world, book, human, theori |
| #17 | citi, area, region, popul, south, world |
| #18 | forc, war, armi, militari, jew, countri |
| #19 | year, first, would, later, time, death |
| #20 | apollo, use, aircraft, flight, mission, first |
Top words of topics generated by gensim | |
|---|---|
| #1 | use, acid, may, also, azerbaijan, cell |
| #2 | use, system, comput, one, also, time |
| #3 | state, citi, day, nation, year, area |
| #4 | state, lincoln, american, war, union, bell |
| #5 | anim, game, anal, atari, area, sex |
| #6 | art, use, work, also, includ, first |
| #7 | american, player, english, politician, footbal, author |
| #8 | new, american, team, season, leagu, year |
| #9 | appl, ii, martin, aston, magnitud, star |
| #10 | bc, assyrian, use, speer, also, abort |
| #11 | use, arsen, also, audi, one, first |
| #12 | algebra, use, set, ture, number, tank |
| #13 | appl, state, use, also, includ, product |
| #14 | use, languag, word, arab, also, english |
| #15 | god, work, one, also, greek, name |
| #16 | first, one, also, time, work, film |
| #17 | church, alexand, arab, also, anglican, use |
| #18 | british, american, new, war, armi, alfr |
| #19 | airlin, vote, candid, approv, footbal, air |
| #20 | apollo, mission, lunar, first, crew, land |
The SIMD instruction set has a great effect on performance. Following is a comparison between SIMD instruction sets.
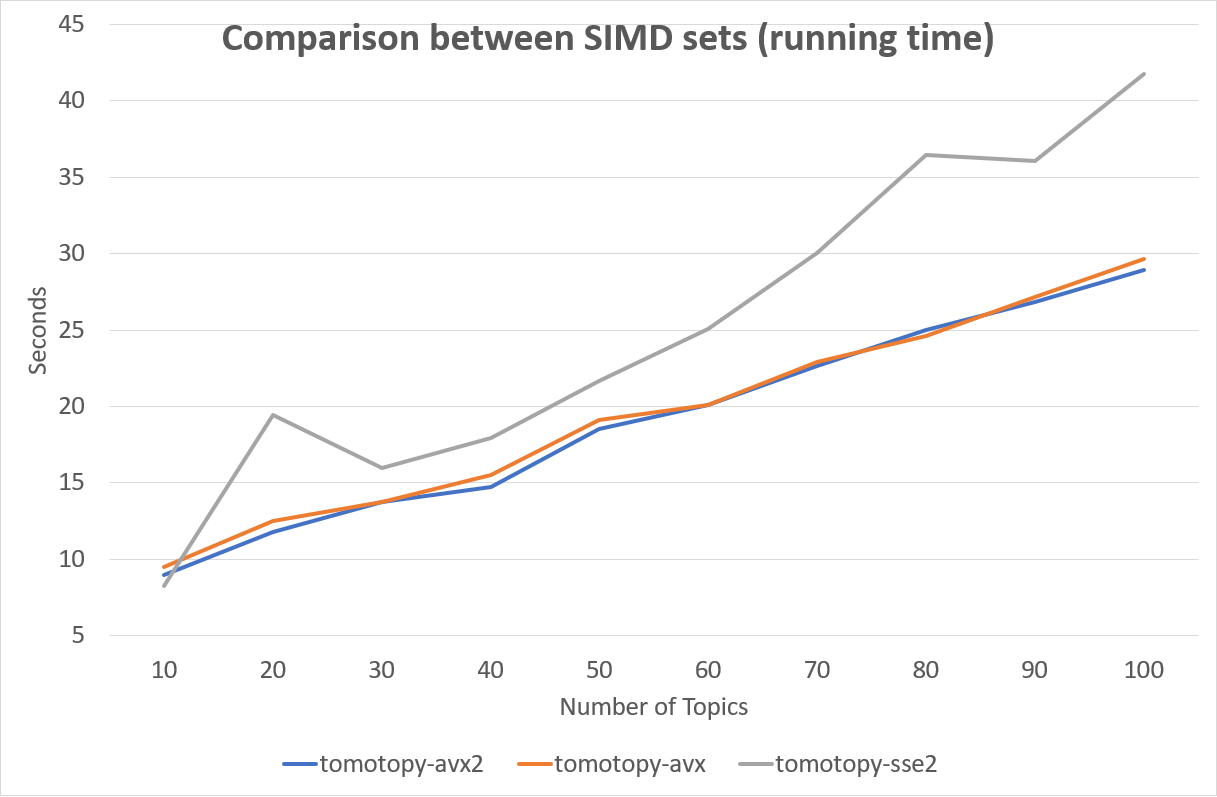
Fortunately, most of recent x86-64 CPUs provide AVX2 instruction set, so we can enjoy the performance of AVX2.
Model Save And Load
tomotopy provides save and load method for each topic model class,
so you can save the model into the file whenever you want, and re-load it from the file.
::
import tomotopy as tp
mdl = tp.HDPModel()
for line in open('sample.txt'):
mdl.add_doc(line.strip().split())
for i in range(0, 100, 10):
mdl.train(10)
print('Iteration: {}\tLog-likelihood: {}'.format(i, mdl.ll_per_word))
# save into file
mdl.save('sample_hdp_model.bin')
# load from file
mdl = tp.HDPModel.load('sample_hdp_model.bin')
for k in range(mdl.k):
if not mdl.is_live_topic(k): continue
print('Top 10 words of topic #{}'.format(k))
print(mdl.get_topic_words(k, top_n=10))
# the saved model is HDP model,
# so when you load it by LDA model, it will raise an exception
mdl = tp.LDAModel.load('sample_hdp_model.bin')
When you load the model from a file, a model type in the file should match the class of methods.
See more at LDAModel.save() and LDAModel.load() methods.
Documents In The Model And Out Of The Model
We can use Topic Model for two major purposes. The basic one is to discover topics from a set of documents as a result of trained model, and the more advanced one is to infer topic distributions for unseen documents by using trained model.
We named the document in the former purpose (used for model training) as document in the model, and the document in the later purpose (unseen document during training) as document out of the model.
In tomotopy, these two different kinds of document are generated differently.
A document in the model can be created by LDAModel.add_doc() method.
add_doc can be called before LDAModel.train() starts.
In other words, after train called, add_doc cannot add a document into the model because the set of document used for training has become fixed.
To acquire the instance of the created document, you should use LDAModel.docs like:
::
mdl = tp.LDAModel(k=20)
idx = mdl.add_doc(words)
if idx < 0: raise RuntimeError("Failed to add doc")
doc_inst = mdl.docs[idx]
# doc_inst is an instance of the added document
A document out of the model is generated by LDAModel.make_doc() method. make_doc can be called only after train starts.
If you use make_doc before the set of document used for training has become fixed, you may get wrong results.
Since make_doc returns the instance directly, you can use its return value for other manipulations.
::
mdl = tp.LDAModel(k=20)
# add_doc ...
mdl.train(100)
doc_inst = mdl.make_doc(unseen_words) # doc_inst is an instance of the unseen document
Inference For Unseen Documents
If a new document is created by LDAModel.make_doc(), its topic distribution can be inferred by the model.
Inference for unseen document should be performed using LDAModel.infer() method.
::
mdl = tp.LDAModel(k=20)
# add_doc ...
mdl.train(100)
doc_inst = mdl.make_doc(unseen_words)
topic_dist, ll = mdl.infer(doc_inst)
print("Topic Distribution for Unseen Docs: ", topic_dist)
print("Log-likelihood of inference: ", ll)
The infer method can infer only one instance of Document or a list of instances of Document.
See more at LDAModel.infer().
Parallel Sampling Algorithms
Since version 0.5.0, tomotopy allows you to choose a parallelism algorithm.
The algorithm provided in versions prior to 0.4.2 is COPY_MERGE, which is provided for all topic models.
The new algorithm PARTITION, available since 0.5.0, makes training generally faster and more memory-efficient, but it is available at not all topic models.
The following chart shows the speed difference between the two algorithms based on the number of topics and the number of workers.
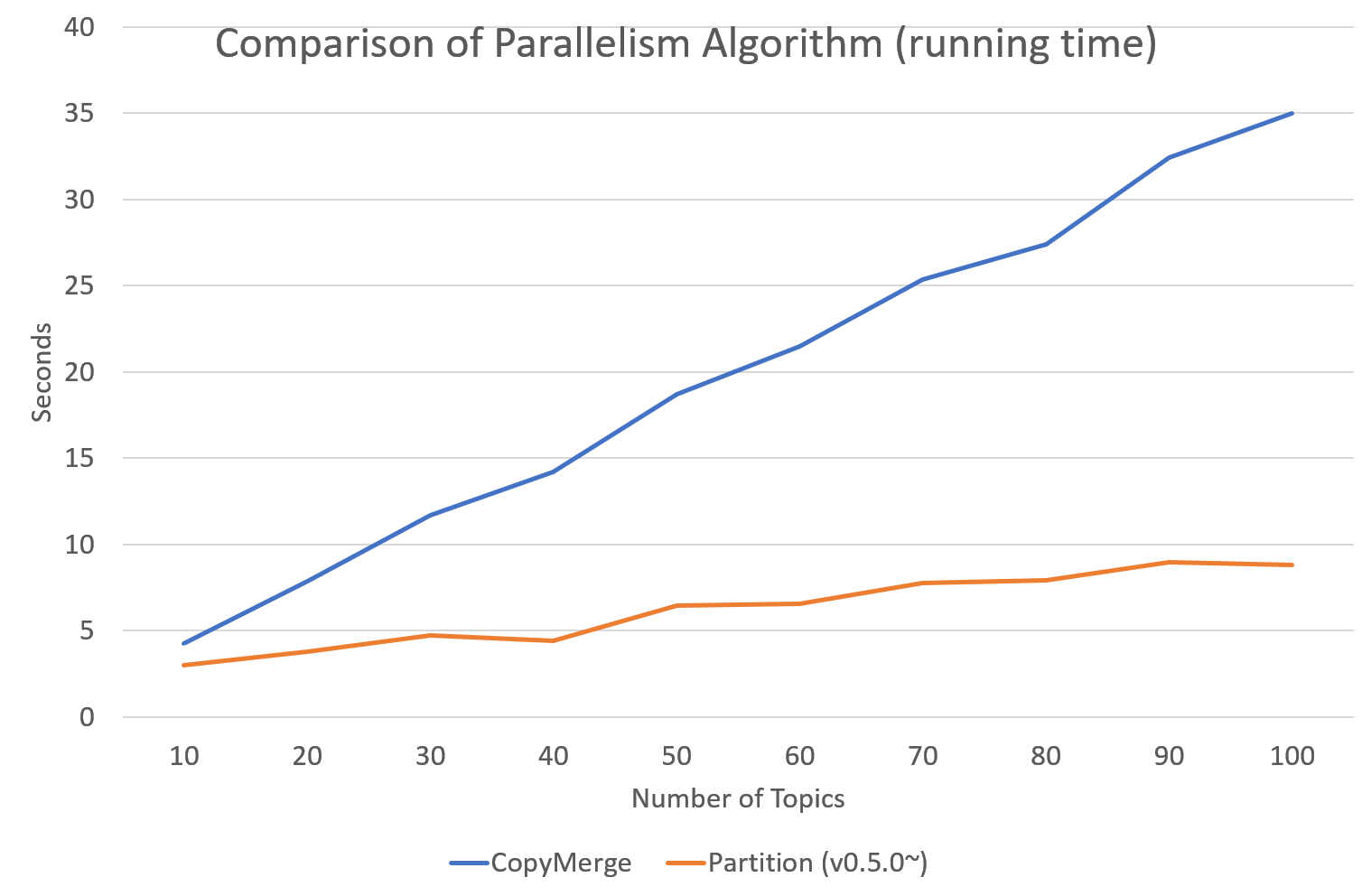
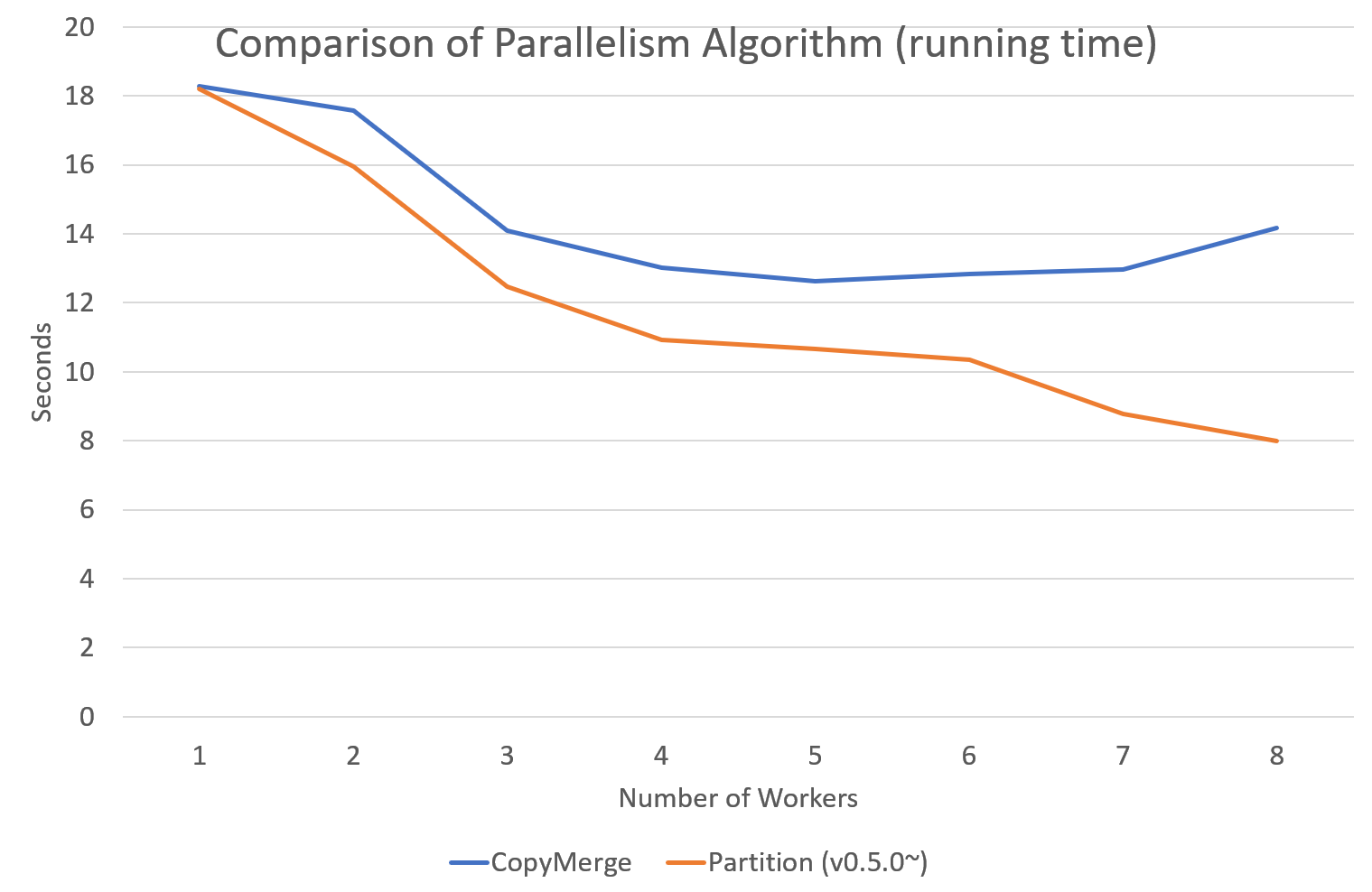
Pining Topics Using Word Priors
Since version 0.6.0, a new method LDAModel.set_word_prior() has been added. It allows you to control word prior for each topic.
For example, we can set the weight of the word 'church' to 1.0 in topic 0, and the weight to 0.1 in the rest of the topics by following codes.
This means that the probability that the word 'church' is assigned to topic 0 is 10 times higher than the probability of being assigned to another topic.
Therefore, most of 'church' is assigned to topic 0, so topic 0 contains many words related to 'church'.
This allows to manipulate some topics to be placed at a specific topic number.
::
import tomotopy as tp
mdl = tp.LDAModel(k=20)
# add documents into <code>mdl</code>
# setting word prior
mdl.set_word_prior('church', [1.0 if k == 0 else 0.1 for k in range(20)])
See word_prior_example in example.py for more details.
Examples
You can find an example python code of tomotopy at https://github.com/bab2min/tomotopy/blob/master/example.py .
You can also get the data file used in the example code at https://drive.google.com/file/d/18OpNijd4iwPyYZ2O7pQoPyeTAKEXa71J/view .
License
tomotopy is licensed under the terms of MIT License,
meaning you can use it for any reasonable purpose and remain in complete ownership of all the documentation you produce.
History
-
0.7.0 (2020-04-18)
DTModelwas added into the package.- A bug in
Corpus.save()was fixed. - A new method
Document.get_count_vector()was added into Document class. - Now linux distributions use manylinux2010 and an additional optimization is applied.
-
0.6.2 (2020-03-28)
- A critical bug related to
saveandloadwas fixed. Version 0.6.0 and 0.6.1 have been removed from releases.
- A critical bug related to
-
0.6.1 (2020-03-22) (removed)
- A bug related to module loading was fixed.
-
0.6.0 (2020-03-22) (removed)
Corpusclass that manages multiple documents easily was added.LDAModel.set_word_prior()method that controls word-topic priors of topic models was added.- A new argument
min_dfthat filters words based on document frequency was added into every topic model's init. tomotopy.label, the submodule about topic labeling was added. Currently, onlyFoRelevanceis provided.
-
0.5.2 (2020-03-01)
- A segmentation fault problem was fixed in
LLDAModel.add_doc(). - A bug was fixed that
inferofHDPModelsometimes crashes the program. - A crash issue was fixed of
LDAModel.infer()with ps=tomotopy.ParallelScheme.PARTITION, together=True.
- A segmentation fault problem was fixed in
-
0.5.1 (2020-01-11)
- A bug was fixed that
SLDAModel.make_doc()doesn't support missing values fory. - Now
SLDAModelfully supports missing values for response variablesy. Documents with missing values (NaN) are included in modeling topic, but excluded from regression of response variables.
- A bug was fixed that
-
0.5.0 (2019-12-30)
- Now
PAModel.infer()returns both topic distribution nd sub-topic distribution. - New methods get_sub_topics and get_sub_topic_dist were added into
Document. (for PAModel) - New parameter
parallelwas added forLDAModel.train()andLDAModel.infer()method. You can select parallelism algorithm by changing this parameter. ParallelScheme.PARTITION, a new algorithm, was added. It works efficiently when the number of workers is large, the number of topics or the size of vocabulary is big.- A bug where
rm_topdidn't work atmin_cf< 2 was fixed.
- Now
-
0.4.2 (2019-11-30)
- Wrong topic assignments of
LLDAModelandPLDAModelwere fixed. - Readable repr of
DocumentandDictionarywas implemented.
- Wrong topic assignments of
-
0.4.1 (2019-11-27)
- A bug at init function of
PLDAModelwas fixed.
- A bug at init function of
-
0.4.0 (2019-11-18)
-
0.3.1 (2019-11-05)
- An issue where
get_topic_dist()returns incorrect value whenmin_cforrm_topis set was fixed. - The return value of
get_topic_dist()ofMGLDAModeldocument was fixed to include local topics. - The estimation speed with
tw=ONEwas improved.
- An issue where
-
0.3.0 (2019-10-06)
- A new model,
LLDAModelwas added into the package. - A crashing issue of
HDPModelwas fixed. - Since hyperparameter estimation for
HDPModelwas implemented, the result ofHDPModelmay differ from previous versions. If you want to turn off hyperparameter estimation of HDPModel, setoptim_intervalto zero.
- A new model,
-
0.2.0 (2019-08-18)
- New models including
CTModelandSLDAModelwere added into the package. - A new parameter option
rm_topwas added for all topic models. - The problems in
saveandloadmethod forPAModelandHPAModelwere fixed. - An occassional crash in loading
HDPModelwas fixed. - The problem that
ll_per_wordwas calculated incorrectly whenmin_cf> 0 was fixed.
- New models including
-
0.1.6 (2019-08-09)
- Compiling errors at clang with macOS environment were fixed.
-
0.1.4 (2019-08-05)
- The issue when
add_docreceives an empty list as input was fixed. - The issue that
PAModel.get_topic_words()doesn't extract the word distribution of subtopic was fixed.
- The issue when
-
0.1.3 (2019-05-19)
- The parameter
min_cfand its stopword-removing function were added for all topic models.
- The parameter
-
0.1.0 (2019-05-12)
- First version of tomotopy
Expand source code
"""
Python package `tomotopy` provides types and functions for various Topic Model
including LDA, DMR, HDP, MG-LDA, PA and HPA. It is written in C++ for speed and provides Python extension.
.. include:: ./documentation.rst
"""
import tomotopy.utils as utils
from enum import IntEnum
class TermWeight(IntEnum):
"""
This enumeration is for Term Weighting Scheme and it is based on following paper:
> * Wilson, A. T., & Chew, P. A. (2010, June). Term weighting schemes for latent dirichlet allocation. In human language technologies: The 2010 annual conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 465-473). Association for Computational Linguistics.
There are three options for term weighting and the basic one is ONE. The others also can be applied for all topic models in `tomotopy`.
"""
ONE = 0
""" Consider every term equal (default)"""
IDF = 1
"""
Use Inverse Document Frequency term weighting.
Thus, a term occurring at almost every document has very low weighting
and a term occurring at a few document has high weighting.
"""
PMI = 2
"""
Use Pointwise Mutual Information term weighting.
"""
class ParallelScheme(IntEnum):
"""
This enumeration is for Parallelizing Scheme:
There are three options for parallelizing and the basic one is DEFAULT. Not all models supports all options.
"""
DEFAULT = 0
"""tomotopy chooses the best available parallelism scheme for your model"""
NONE = 1
"""
Turn off multi-threading for Gibbs sampling at training or inference. Operations other than Gibbs sampling may use multithreading.
"""
COPY_MERGE = 2
"""
Use Copy and Merge algorithm from AD-LDA. It consumes RAM in proportion to the number of workers.
This has advantages when you have a small number of workers and a small number of topics and vocabulary sizes in the model.
Prior to version 0.5, all models used this algorithm by default.
> * Newman, D., Asuncion, A., Smyth, P., & Welling, M. (2009). Distributed algorithms for topic models. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(Aug), 1801-1828.
"""
PARTITION = 3
"""
Use Partitioning algorithm from PCGS. It consumes only twice as much RAM as a single-threaded algorithm, regardless of the number of workers.
This has advantages when you have a large number of workers or a large number of topics and vocabulary sizes in the model.
> * Yan, F., Xu, N., & Qi, Y. (2009). Parallel inference for latent dirichlet allocation on graphics processing units. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 2134-2142).
"""
isa = ''
"""
Indicate which SIMD instruction set is used for acceleration.
It can be one of `'avx2'`, `'avx'`, `'sse2'` and `'none'`.
"""
# This code is an autocomplete-hint for IDE.
# The object imported here will be overwritten by _load() function.
try: from _tomotopy import *
except: pass
def _load():
import importlib, os
from cpuinfo import get_cpu_info
flags = get_cpu_info()['flags']
env_setting = os.environ.get('TOMOTOPY_ISA', '').split(',')
if not env_setting[0]: env_setting = []
isas = ['avx2', 'avx', 'sse2', 'none']
isas = [isa for isa in isas if (env_setting and isa in env_setting) or (not env_setting and (isa in flags or isa == 'none'))]
if not isas: raise RuntimeError("No isa option for " + str(env_setting))
for isa in isas:
try:
mod_name = '_tomotopy' + ('_' + isa if isa != 'none' else '')
globals().update({k:v for k, v in vars(importlib.import_module(mod_name)).items() if not k.startswith('_')})
return
except:
if isa == isas[-1]: raise
_load()
import os
if os.environ.get('TOMOTOPY_LANG') == 'kr':
__doc__ = """`tomotopy` 패키지는 Python에서 사용가능한 다양한 토픽 모델링 타입과 함수를 제공합니다.
내부 모듈은 c++로 작성되었기 때문에 빠른 속도를 자랑합니다.
.. include:: ./documentation.kr.rst
"""
__pdoc__ = {}
__pdoc__['isa'] = """현재 로드된 모듈이 어떤 SIMD 명령어 세트를 사용하는지 표시합니다.
이 값은 `'avx2'`, `'avx'`, `'sse2'`, `'none'` 중 하나입니다."""
__pdoc__['TermWeight'] = """용어 가중치 기법을 선택하는 데에 사용되는 열거형입니다. 여기에 제시된 용어 가중치 기법들은 다음 논문을 바탕으로 하였습니다:
> * Wilson, A. T., & Chew, P. A. (2010, June). Term weighting schemes for latent dirichlet allocation. In human language technologies: The 2010 annual conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 465-473). Association for Computational Linguistics.
총 3가지 가중치 기법을 사용할 수 있으며 기본값은 ONE입니다. 기본값뿐만 아니라 다른 모든 기법들도 `tomotopy`의 모든 토픽 모델에 사용할 수 있습니다. """
__pdoc__['TermWeight.ONE'] = """모든 용어를 동일하게 간주합니다. (기본값)"""
__pdoc__['TermWeight.IDF'] = """역문헌빈도(IDF)를 가중치로 사용합니다.
따라서 모든 문헌에 거의 골고루 등장하는 용어의 경우 낮은 가중치를 가지게 되며,
소수의 특정 문헌에만 집중적으로 등장하는 용어의 경우 높은 가중치를 가지게 됩니다."""
__pdoc__['TermWeight.PMI'] = """점별 상호정보량(PMI)을 가중치로 사용합니다."""
__pdoc__['ParallelScheme'] = """병렬화 기법을 선택하는 데에 사용되는 열거형입니다. 총 3가지 기법을 사용할 수 있으나, 모든 모델이 아래의 기법을 전부 지원하지는 않습니다."""
__pdoc__['ParallelScheme.DEFAULT'] = """tomotopy가 모델에 따라 적합한 병럴화 기법을 선택하도록 합니다. 이 값이 기본값입니다."""
__pdoc__['ParallelScheme.NONE'] = """깁스 샘플링에 병렬화 기법을 사용하지 않습니다. 깁스 샘플링을 제외한 다른 연산들은 여전히 병렬로 처리될 수 있습니다."""
__pdoc__['ParallelScheme.COPY_MERGE'] = """
AD-LDA에서 제안된 복사 후 합치기 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 이는 작업자 수에 비례해 메모리를 소모합니다.
작업자 수가 적거나, 토픽 개수 혹은 어휘 집합의 크기가 작을 때 유리합니다.
0.5버전 이전까지는 모든 모델은 이 알고리즘을 기본으로 사용했습니다.
> * Newman, D., Asuncion, A., Smyth, P., & Welling, M. (2009). Distributed algorithms for topic models. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(Aug), 1801-1828.
"""
__pdoc__['ParallelScheme.PARTITION'] = """
PCGS에서 제안된 분할 샘플링 알고리즘을 사용합니다. 작업자 수에 관계없이 단일 스레드 알고리즘에 비해 2배의 메모리만 소모합니다.
작업자 수가 많거나, 토픽 개수 혹은 어휘 집합의 크기가 클 때 유리합니다.
> * Yan, F., Xu, N., & Qi, Y. (2009). Parallel inference for latent dirichlet allocation on graphics processing units. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 2134-2142).
"""
del _load, IntEnum, osSub-modules
tomotopy.label-
Submodule
tomotopy.labelprovides automatic topic labeling techniques. You can label topics automatically with simple code like below. The results … tomotopy.utils-
Submodule
tomotopy.utilsprovides various utilities for topic modeling.Corpusclass helps manage multiple documents easily. The …
Global variables
var isa-
Indicate which SIMD instruction set is used for acceleration. It can be one of
'avx2','avx','sse2'and'none'.
Classes
class CTModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k=1, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
Added in version: 0.2.0
This type provides Correlated Topic Model (CTM) and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Blei, D., & Lafferty, J. (2006). Correlated topic models. Advances in neural information processing systems, 18, 147.
- Mimno, D., Wallach, H., & McCallum, A. (2008, December). Gibbs sampling for logistic normal topic models with graph-based priors. In NIPS Workshop on Analyzing Graphs (Vol. 61).
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int- the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k:int- the number of topics between 1 ~ 32767.
alpha:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
seed:int- random seed. The default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var num_beta_sample-
the number of times to sample beta parameters, default value is 10.
CTModel samples
num_beta_samplebeta parameters for each document. The more beta it samples, the more accurate the distribution will be, but the longer time it takes to learn. If you have a small number of documents in your model, keeping this value larger will help you get better result. var num_tmn_sample-
the number of iterations for sampling Truncated Multivariate Normal distribution, default value is 5.
If your model shows biased topic correlations, increasing this value may be helpful.
var prior_cov-
the covariance matrix of prior logistic-normal distribution the for topic distribution (read-only)
var prior_mean-
the mean of prior logistic-normal distribution for the topic distribution (read-only)
Methods
def get_correlations(self, topic_id)-
Return correlations between the topic
topic_idand other topics. The returned value is alistoffloats of sizeLDAModel.k.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k), indicating the topic
Inherited members
class DMRModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k=1, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, sigma=1.0, alpha_epsilon=1e-10, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Dirichlet Multinomial Regression(DMR) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Mimno, D., & McCallum, A. (2012). Topic models conditioned on arbitrary features with dirichlet-multinomial regression. arXiv preprint arXiv:1206.3278.
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int-
Added in version: 0.2.0
the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k:int- the number of topics between 1 ~ 32767
alpha:float- exponential of mean of normal distribution for
lambdas eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic - word
sigma:float- standard deviation of normal distribution for
lambdas alpha_epsilon:float- small smoothing value for preventing
exp(lambdas)to be zero seed:int- random seed. default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var alpha_epsilon-
the smooting value alpha-epsilon (read-only)
var f-
the number of metadata features (read-only)
var lambdas-
a
listof paramter lambdas (read-only) var metadata_dict-
a dictionary of metadata in type
Dictionary(read-only) var sigma-
the hyperparamter sigma (read-only)
Methods
def add_doc(self, words, metadata='')-
Add a new document into the model instance with
metadataand return an index of the inserted document.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str metadata:str- metadata of the document (e.g., author, title or year)
def make_doc(self, words, metadata='')-
Return a new
Documentinstance for an unseen document withwordsandmetadatathat can be used forLDAModel.infer()method.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iteratable of
str metadata:str- metadata of the document (e.g., author, title or year)
Inherited members
class DTModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k=1, t=1, alpha_var=0.1, eta_var=0.1, phi_var=0.1, lr_a=0.01, lr_b=0.1, lr_c=0.55, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Dynamic Topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Blei, D. M., & Lafferty, J. D. (2006, June). Dynamic topic models. In Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning (pp. 113-120).
- Bhadury, A., Chen, J., Zhu, J., & Liu, S. (2016, April). Scaling up dynamic topic models. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web (pp. 381-390). https://github.com/Arnie0426/FastDTM
Added in version: 0.7.0
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int- minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int- the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k:int- the number of topics between 1 ~ 32767
t:int- the number of timpoints
alpha_var:float- transition variance of alpha (per-document topic distribution)
eta_var:float- variance of eta (topic distribution of each document) from its alpha
phi_var:float- transition variance of phi (word distribution of each topic)
lr_a:float- shape parameter
agreater than zero, for SGLD step size calculated ase_i = a * (b + i) ^ (-c) lr_b:float- shape parameter
bgreater than or equal to zero, for SGLD step size calculated ase_i = a * (b + i) ^ (-c) lr_c:float- shape parameter
cwith range (0.5, 1], for SGLD step size calculated ase_i = a * (b + i) ^ (-c) seed:int- random seed. default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus- a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]- a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var lr_a-
parameter
agreater than zero for SGLD step size (e_i = a * (b + i) ^ -c) var lr_b-
parameter
bgreater than zero or equal to zero for SGLD step size (e_i = a * (b + i) ^ -c) var lr_c-
parameter
cwith range (0.5, 1] for SGLD step size (e_i = a * (b + i) ^ -c)
Methods
def add_doc(self, words, timepoint=0)-
Add a new document into the model instance with
timepointand return an index of the inserted document.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str timepoint:int- an integer with range [0,
t)
def get_alpha(self, timepoint)-
Return a
listof alpha parameters fortimepoint.Parameters
timepoint:int- an integer with range [0,
t)
def get_phi(self, timepoint, topic_id)-
Return a
listof phi parameters fortimepointandtopic_id.Parameters
timepoint:int- an integer with range [0,
t) topic_id:int- an integer with range [0,
k)
def get_topic_word_dist(self, topic_id, timepoint)-
Return the word distribution of the topic
topic_idwithtimepoint. The returned value is alistthat haslen(vocabs)fraction numbers indicating probabilities for each word in the current topic.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic timepoint:int- an integer in range [0,
t), indicating the timepoint
def get_topic_words(self, topic_id, timepoint, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_nwords and its probability in the topictopic_idwithtimepoint. The return type is alistof (word:str, probability:float).Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k), indicating the topic timepoint:int- an integer in range [0,
t), indicating the timepoint
def make_doc(self, words, timepoint=0)-
Return a new
Documentinstance for an unseen document withwordsandtimepointthat can be used forLDAModel.infer()method.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iteratable of
str timepoint:int- an integer with range [0,
t)
Inherited members
class Dictionary (...)-
list-like Dictionary interface for vocabularies class Document-
This type provides abstract model to access documents to be used Topic Model.
An instance of this type can be acquired from
LDAModel.make_doc()method orLDAModel.docsmember of each Topic Model instance.Instance variables
var beta-
a
listof beta parameters for each topic (for onlyCTModelmodel, read-only)Added in version: 0.2.0
var eta-
a
listof eta parameters(topic distribution) for the current document (for onlyDTModelmodel, read-only)Added in version: 0.7.0
var labelsvar metadata-
"metadata of the document (for only
DMRModelmodel, read-only) var subtopicsvar timepoint-
a timepoint of the document (for only
DTModelmodel, read-only)Added in version: 0.7.0
var topicsvar vars-
a
listof response variables (for onlySLDAModelmodel, read-only)Added in version: 0.2.0
var weight-
a weight of the document (read-only)
var windows-
a
listof window IDs for each word (for onlyMGLDAModelmodel, read-only) var words-
a
listof IDs for each word (read-only)
Methods
def get_count_vector(self)-
Added in version: 0.7.0
Return a count vector for the current document.
def get_sub_topic_dist(self)-
Added in version: 0.5.0
Return a distribution of the sub topics in the document. (for only
PAModel) def get_sub_topics(self, top_n=10)-
Added in version: 0.5.0
Return the
top_nsub topics with its probability of the document. (for onlyPAModel) def get_topic_dist(self)-
Return a distribution of the topics in the document.
def get_topics(self, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_ntopics with its probability of the document. def get_words(self, top_n=10)-
Added in version: 0.4.2
Return the
top_nwords with its probability of the document.
class HDPModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, initial_k=2, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, gamma=0.1, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Hierarchical Dirichlet Process(HDP) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Teh, Y. W., Jordan, M. I., Beal, M. J., & Blei, D. M. (2005). Sharing clusters among related groups: Hierarchical Dirichlet processes. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 1385-1392).
- Newman, D., Asuncion, A., Smyth, P., & Welling, M. (2009). Distributed algorithms for topic models. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(Aug), 1801-1828.
Since version 0.3.0, hyperparameter estimation for
alphaandgammahas been added. You can turn off this estimation by settingoptim_intervalto zero.Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int-
Added in version: 0.2.0
the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
initial_k:int- the initial number of topics between 2 ~ 32767.
The number of topics will be adjusted for data during training.
Since version 0.3.0, the default value has been changed to 2 from 1. alpha:float- concentration coeficient of Dirichlet Process for document-table
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
gamma:float- concentration coeficient of Dirichlet Process for table-topic
seed:int- random seed. default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var gamma-
the hyperparameter gamma (read-only)
var live_k-
the number of alive topics (read-only)
var num_tables-
the number of total tables (read-only)
Methods
def is_live_topic(self, topic_id)-
Return
Trueif the topictopic_idis alive, otherwise returnFalse.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic
Inherited members
class HLDAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, depth=2, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, gamma=0.1, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Hierarchical LDA topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Griffiths, T. L., Jordan, M. I., Tenenbaum, J. B., & Blei, D. M. (2004). Hierarchical topic models and the nested Chinese restaurant process. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 17-24).
Added in version: 0.4.0
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int- the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
depth:int- the maximum depth level of hierarchy between 2 ~ 32767.
alpha:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
gamma:float- concentration coeficient of Dirichlet Process
seed:int- random seed. default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var depth-
the number of depth (read-only)
var gamma-
the hyperparameter gamma (read-only)
var live_k-
the number of alive topics (read-only)
Methods
def children_topics(self, topic_id)-
Return a list of topic IDs with children of a topic
topic_id.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic
def is_live_topic(self, topic_id)-
Return
Trueif the topictopic_idis alive, otherwise returnFalse.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic
def level(self, topic_id)-
Return the level of a topic
topic_id.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic
def num_docs_of_topic(self, topic_id)-
Return the number of documents belonging to a topic
topic_id.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic
def parent_topic(self, topic_id)-
Return the topic ID of parent of a topic
topic_id.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic
Inherited members
class HPAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k1=1, k2=1, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Hierarchical Pachinko Allocation(HPA) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Mimno, D., Li, W., & McCallum, A. (2007, June). Mixtures of hierarchical topics with pachinko allocation. In Proceedings of the 24th international conference on Machine learning (pp. 633-640). ACM.
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int-
Added in version: 0.2.0
the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k1:int- the number of super topics between 1 ~ 32767
k2:int- the number of sub topics between 1 ~ 32767
alpha:float- initial hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
seed:int- random seed. default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Methods
def get_topic_word_dist(self, topic_id)-
Return the word distribution of the topic
topic_id. The returned value is alistthat haslen(vocabs)fraction numbers indicating probabilities for each word in current topic.Parameters
topic_id:int- 0 indicates the top topic,
a number in range [1, 1 +
k1) indicates a super topic and a number in range [1 +k1, 1 +k1+k2) indicates a sub topic.
def get_topic_words(self, topic_id, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_nwords and its probability in the topictopic_id. The return type is alistof (word:str, probability:float).Parameters
topic_id:int- 0 indicates the top topic,
a number in range [1, 1 +
k1) indicates a super topic and a number in range [1 +k1, 1 +k1+k2) indicates a sub topic.
def infer(self, doc, iter=100, tolerance=-1, workers=0, parallel=0, together=False)-
Return the inferred topic distribution from unseen
docs. The return type is (a topic distribution ofdoc, log likelihood) or (alistof topic distribution ofdoc, log likelihood)Parameters
doc:Union[Document, Iterable[Document]]- an instance of
Documentor alistof instances ofDocumentto be inferred by the model. It can be acquired fromLDAModel.make_doc()method. iter:int- an integer indicating the number of iteration to estimate the distribution of topics of
doc. The higher value will generate a more accuracy result. tolerance:float- isn't currently used.
workers:int- an integer indicating the number of workers to perform samplings.
If
workersis 0, the number of cores in the system will be used. parallel:Union[int, ParallelScheme]-
Added in version: 0.5.0
the parallelism scheme for inference. the default value is ParallelScheme.DEFAULT which means that tomotopy selects the best scheme by model.
together:bool- all
docs are infered together in one process if True, otherwise eachdocis infered independently. Its default value isFalse.
Inherited members
class LDAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k=1, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Latent Dirichlet Allocation(LDA) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Blei, D.M., Ng, A.Y., &Jordan, M.I. (2003).Latent dirichlet allocation.Journal of machine Learning research, 3(Jan), 993 - 1022.
- Newman, D., Asuncion, A., Smyth, P., &Welling, M. (2009).Distributed algorithms for topic models.Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(Aug), 1801 - 1828.
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int-
Added in version: 0.2.0
the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k:int- the number of topics between 1 ~ 32767.
alpha:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
seed:int- random seed. The default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Subclasses
Static methods
def load(filename)-
Return the model instance loaded from file
filename.
Instance variables
var alpha-
the hyperparameter alpha (read-only)
var burn_in-
get or set the burn-in iterations for optimizing parameters
Its default value is 0.
var docs-
a
list-like interface ofDocumentin the model instance (read-only) var eta-
the hyperparameter eta (read-only)
var k-
K, the number of topics (read-only)
var ll_per_word-
a log likelihood per-word of the model (read-only)
var num_vocabs-
the number of vocabuluaries after words with a smaller frequency were removed (read-only)
This value is 0 before
traincalled. var num_words-
the number of total words (read-only)
This value is 0 before
traincalled. var optim_interval-
get or set the interval for optimizing parameters
Its default value is 10. If it is set to 0, the parameter optimization is turned off.
var perplexity-
a perplexity of the model (read-only)
var removed_top_words-
a
listofstrwhich is a word removed from the model if you setrm_topgreater than 0 at initializing the model (read-only) var tw-
the term weighting scheme (read-only)
var vocab_freq-
a
listof vocabulary frequencies included in the model (read-only) var vocabs-
a dictionary of vocabuluary as type
Dictionary(read-only)
Methods
def add_doc(self, words)-
Add a new document into the model instance and return an index of the inserted document. This method should be called before calling the
LDAModel.train().Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str
def get_count_by_topics(self)-
Return the number of words allocated to each topic.
def get_topic_word_dist(self, topic_id)-
Return the word distribution of the topic
topic_id. The returned value is alistthat haslen(vocabs)fraction numbers indicating probabilities for each word in the current topic.Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k) indicating the topic
def get_topic_words(self, topic_id, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_nwords and its probability in the topictopic_id. The return type is alistof (word:str, probability:float).Parameters
topic_id:int- an integer in range [0,
k), indicating the topic
def get_word_prior(self, word)-
Added in version: 0.6.0
Return word-topic prior for
word. If there is no set prior forword, an empty list is returned.Parameters
word:str- a word
def infer(self, doc, iter=100, tolerance=-1, workers=0, parallel=0, together=False)-
Return the inferred topic distribution from unseen
docs. The return type is (a topic distribution ofdoc, log likelihood) or (alistof topic distribution ofdoc, log likelihood)Parameters
doc:Union[Document, Iterable[Document]]- an instance of
Documentor alistof instances ofDocumentto be inferred by the model. It can be acquired fromLDAModel.make_doc()method. iter:int- an integer indicating the number of iteration to estimate the distribution of topics of
doc. The higher value will generate a more accuracy result. tolerance:float- isn't currently used.
workers:int- an integer indicating the number of workers to perform samplings.
If
workersis 0, the number of cores in the system will be used. parallel:Union[int, ParallelScheme]-
Added in version: 0.5.0
the parallelism scheme for inference. the default value is ParallelScheme.DEFAULT which means that tomotopy selects the best scheme by model.
together:bool- all
docs are infered together in one process if True, otherwise eachdocis infered independently. Its default value isFalse.
def make_doc(self, words)-
Return a new
Documentinstance for an unseen document withwordsthat can be used forLDAModel.infer()method.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str
def save(self, filename, full=True)-
Save the model instance to file
filename. ReturnNone.If
fullisTrue, the model with its all documents and state will be saved. If you want to train more after, use full model. IfFalse, only topic paramters of the model will be saved. This model can be only used for inference of an unseen document.Added in version: 0.6.0
Since version 0.6.0, the model file format has been changed. Thus model files saved in version 0.6.0 or later are not compatible with versions prior to 0.5.2.
def set_word_prior(self, word, prior)-
Added in version: 0.6.0
Set word-topic prior. This method should be called before calling the
LDAModel.train().Parameters
word:str- a word to be set
prior:Iterable[float]- topic distribution of
wordwhose length is equal toLDAModel.k
def train(self, iter=10, workers=0, parallel=0)-
Train the model using Gibbs-sampling with
iteriterations. ReturnNone. After calling this method, you cannotLDAModel.add_doc()orLDAModel.set_word_prior()more.Parameters
iter:int- the number of iterations of Gibbs-sampling
workers:int- an integer indicating the number of workers to perform samplings.
If
workersis 0, the number of cores in the system will be used. parallel:Union[int, ParallelScheme]-
Added in version: 0.5.0
the parallelism scheme for training. the default value is ParallelScheme.DEFAULT which means that tomotopy selects the best scheme by model.
class LLDAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k=1, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Labeled LDA(L-LDA) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Ramage, D., Hall, D., Nallapati, R., & Manning, C. D. (2009, August). Labeled LDA: A supervised topic model for credit attribution in multi-labeled corpora. In Proceedings of the 2009 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Volume 1-Volume 1 (pp. 248-256). Association for Computational Linguistics.
Added in version: 0.3.0
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int- the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k:int- the number of topics between 1 ~ 32767.
alpha:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
seed:int- random seed. The default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var topic_label_dict-
a dictionary of topic labels in type
Dictionary(read-only)
Methods
def add_doc(self, words, labels=[])-
Add a new document into the model instance with
labelsand return an index of the inserted document.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str labels:Iterable[str]- labels of the document
def get_topic_words(self, topic_id, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_nwords and its probability in the topictopic_id. The return type is alistof (word:str, probability:float).Parameters
topic_id:int- Integers in the range [0,
l), wherelis the number of total labels, represent a topic that belongs to the corresponding label. The label name can be found by looking upLLDAModel.topic_label_dict. Integers in the range [l,k) represent a latent topic which doesn't belongs to the any labels.
def make_doc(self, words, labels=[])-
Return a new
Documentinstance for an unseen document withwordsandlabelsthat can be used forLDAModel.infer()method.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iteratable of
str labels:Iterable[str]- labels of the document
Inherited members
class MGLDAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k_g=1, k_l=1, t=3, alpha_g=0.1, alpha_l=0.1, alpha_mg=0.1, alpha_ml=0.1, eta_g=0.01, eta_l=0.01, gamma=0.1, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Multi Grain Latent Dirichlet Allocation(MG-LDA) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Titov, I., & McDonald, R. (2008, April). Modeling online reviews with multi-grain topic models. In Proceedings of the 17th international conference on World Wide Web (pp. 111-120). ACM.
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int-
Added in version: 0.2.0
the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k_g:int- the number of global topics between 1 ~ 32767
k_l:int- the number of local topics between 1 ~ 32767
t:int- the size of sentence window
alpha_g:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-global topic
alpha_l:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-local topic
alpha_mg:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for global-local selection (global coef)
alpha_ml:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for global-local selection (local coef)
eta_g:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for global topic-word
eta_l:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for local topic-word
gamma:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for sentence-window
seed:int- random seed. default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var alpha_g-
the hyperparamter alpha_g (read-only)
var alpha_l-
the hyperparamter alpha_l (read-only)
var alpha_mg-
the hyperparamter alpha_mg (read-only)
var alpha_ml-
the hyperparamter alpha_ml (read-only)
var eta_g-
the hyperparamter eta_g (read-only)
var eta_l-
the hyperparamter eta_l (read-only)
var gamma-
the hyperparamter gamma (read-only)
var k_g-
the hyperparamter k_g (read-only)
var k_l-
the hyperparamter k_l (read-only)
var t-
the hyperparamter t (read-only)
Methods
def add_doc(self, words, delimiter='.')-
Add a new document into the model instance and return an index of the inserted document.
Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str delimiter:str- a sentence separator.
wordswill be separated by this value into sentences.
def get_topic_word_dist(self, topic_id)-
Return the word distribution of the topic
topic_id. The returned value is alistthat haslen(vocabs)fraction numbers indicating probabilities for each word in the current topic.Parameters
topic_id:int- A number in range [0,
k_g) indicates a global topic and a number in range [k_g,k_g+k_l) indicates a local topic.
def get_topic_words(self, topic_id, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_nwords and its probability in the topictopic_id. The return type is alistof (word:str, probability:float).Parameters
topic_id:int- A number in range [0,
k_g) indicates a global topic and a number in range [k_g,k_g+k_l) indicates a local topic.
def make_doc(self, words, delimiter='.')-
Return a new
Documentinstance for an unseen document withwordsthat can be used forLDAModel.infer()method.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iteratable of
str delimiter:str- a sentence separator.
wordswill be separated by this value into sentences.
Inherited members
class PAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k1=1, k2=1, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Pachinko Allocation(PA) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Li, W., & McCallum, A. (2006, June). Pachinko allocation: DAG-structured mixture models of topic correlations. In Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on Machine learning (pp. 577-584). ACM.
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int-
Added in version: 0.2.0
the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k1:int- the number of super topics between 1 ~ 32767
k2:int- the number of sub topics between 1 ~ 32767
alpha:float- initial hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-super topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for sub topic-word
seed:int- random seed. default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Subclasses
Instance variables
var k1-
k1, the number of super topics (read-only)
var k2-
k2, the number of sub topics (read-only)
Methods
def get_sub_topic_dist(self, super_topic_id)-
Return a distribution of the sub topics in a super topic
super_topic_id. The returned value is alistthat hask2fraction numbers indicating probabilities for each sub topic in the current super topic.Parameters
super_topic_id:int- indicating the super topic, in range [0,
k1)
def get_sub_topics(self, super_topic_id, top_n=10)-
Added in version: 0.1.4
Return the
top_nsub topics and its probability in a super topicsuper_topic_id. The return type is alistof (subtopic:int, probability:float).Parameters
super_topic_id:int- indicating the super topic, in range [0,
k1)
def get_topic_word_dist(self, sub_topic_id)-
Return the word distribution of the sub topic
sub_topic_id. The returned value is alistthat haslen(vocabs)fraction numbers indicating probabilities for each word in the current sub topic.Parameters
sub_topic_id:int- indicating the sub topic, in range [0,
k2)
def get_topic_words(self, sub_topic_id, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_nwords and its probability in the sub topicsub_topic_id. The return type is alistof (word:str, probability:float).Parameters
sub_topic_id:int- indicating the sub topic, in range [0,
k2)
def infer(self, doc, iter=100, tolerance=-1, workers=0, parallel=0, together=False)-
Added in version: 0.5.0
Return the inferred topic distribution and sub-topic distribution from unseen
docs. The return type is ((a topic distribution ofdoc, a sub-topic distribution ofdoc), log likelihood) or (alistof (topic distribution ofdoc, sub-topic distribution ofdoc), log likelihood)Parameters
doc:Union[Document, Iterable[Document]]- an instance of
Documentor alistof instances ofDocumentto be inferred by the model. It can be acquired fromLDAModel.make_doc()method. iter:int- an integer indicating the number of iteration to estimate the distribution of topics of
doc. The higher value will generate a more accuracy result. tolerance:float- isn't currently used.
workers:int- an integer indicating the number of workers to perform samplings.
If
workersis 0, the number of cores in the system will be used. parallel:Union[int, ParallelScheme]-
Added in version: 0.5.0
the parallelism scheme for inference. the default value is ParallelScheme.DEFAULT which means that tomotopy selects the best scheme by model.
together:bool- all
docs are infered together in one process if True, otherwise eachdocis infered independently. Its default value isFalse.
Inherited members
class PLDAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k=1, alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides Partially Labeled LDA(PLDA) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Ramage, D., Manning, C. D., & Dumais, S. (2011, August). Partially labeled topic models for interpretable text mining. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 457-465). ACM.
Added in version: 0.4.0
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int- the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
latent_topics:int- the number of latent topics, which are shared to all documents, between 1 ~ 32767.
topics_per_label:int- the number of topics per label between 1 ~ 32767.
alpha:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
seed:int- random seed. The default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var latent_topics-
the number of latent topics (read-only)
var topic_label_dict-
a dictionary of topic labels in type
Dictionary(read-only) var topics_per_label-
the number of topics per label (read-only)
Methods
def add_doc(self, words, labels=[])-
Add a new document into the model instance with
labelsand return an index of the inserted document.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str labels:Iterable[str]- labels of the document
def get_topic_words(self, topic_id, top_n=10)-
Return the
top_nwords and its probability in the topictopic_id. The return type is alistof (word:str, probability:float).Parameters
topic_id:int- Integers in the range [0,
l*topics_per_label), wherelis the number of total labels, represent a topic that belongs to the corresponding label. The label name can be found by looking upPLDAModel.topic_label_dict. Integers in the range [l*topics_per_label,l*topics_per_label+latent_topics) represent a latent topic which doesn't belongs to the any labels.
def make_doc(self, words, labels=[])-
Return a new
Documentinstance for an unseen document withwordsandlabelsthat can be used forLDAModel.infer()method.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iteratable of
str labels:Iterable[str]- labels of the document
Inherited members
class ParallelScheme (value, names=None, *, module=None, qualname=None, type=None, start=1)-
This enumeration is for Parallelizing Scheme: There are three options for parallelizing and the basic one is DEFAULT. Not all models supports all options.
Expand source code
class ParallelScheme(IntEnum): """ This enumeration is for Parallelizing Scheme: There are three options for parallelizing and the basic one is DEFAULT. Not all models supports all options. """ DEFAULT = 0 """tomotopy chooses the best available parallelism scheme for your model""" NONE = 1 """ Turn off multi-threading for Gibbs sampling at training or inference. Operations other than Gibbs sampling may use multithreading. """ COPY_MERGE = 2 """ Use Copy and Merge algorithm from AD-LDA. It consumes RAM in proportion to the number of workers. This has advantages when you have a small number of workers and a small number of topics and vocabulary sizes in the model. Prior to version 0.5, all models used this algorithm by default. > * Newman, D., Asuncion, A., Smyth, P., & Welling, M. (2009). Distributed algorithms for topic models. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(Aug), 1801-1828. """ PARTITION = 3 """ Use Partitioning algorithm from PCGS. It consumes only twice as much RAM as a single-threaded algorithm, regardless of the number of workers. This has advantages when you have a large number of workers or a large number of topics and vocabulary sizes in the model. > * Yan, F., Xu, N., & Qi, Y. (2009). Parallel inference for latent dirichlet allocation on graphics processing units. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 2134-2142). """Ancestors
- enum.IntEnum
- builtins.int
- enum.Enum
Class variables
var COPY_MERGE-
Use Copy and Merge algorithm from AD-LDA. It consumes RAM in proportion to the number of workers. This has advantages when you have a small number of workers and a small number of topics and vocabulary sizes in the model. Prior to version 0.5, all models used this algorithm by default.
- Newman, D., Asuncion, A., Smyth, P., & Welling, M. (2009). Distributed algorithms for topic models. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(Aug), 1801-1828.
var DEFAULT-
tomotopy chooses the best available parallelism scheme for your model
var NONE-
Turn off multi-threading for Gibbs sampling at training or inference. Operations other than Gibbs sampling may use multithreading.
var PARTITION-
Use Partitioning algorithm from PCGS. It consumes only twice as much RAM as a single-threaded algorithm, regardless of the number of workers. This has advantages when you have a large number of workers or a large number of topics and vocabulary sizes in the model.
- Yan, F., Xu, N., & Qi, Y. (2009). Parallel inference for latent dirichlet allocation on graphics processing units. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 2134-2142).
class SLDAModel (tw=TermWeight.ONE, min_cf=0, min_df=0, rm_top=0, k=1, vars='', alpha=0.1, eta=0.01, mu=[], nu_sq=[], glm_param=[], seed=None, corpus=None, transform=None)-
This type provides supervised Latent Dirichlet Allocation(sLDA) topic model and its implementation is based on following papers:
- Mcauliffe, J. D., & Blei, D. M. (2008). Supervised topic models. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 121-128).
- Python version implementation using Gibbs sampling : https://github.com/Savvysherpa/slda
Added in version: 0.2.0
Parameters
tw:Union[int, TermWeight]- term weighting scheme in
TermWeight. The default value is TermWeight.ONE min_cf:int- minimum collection frequency of words. Words with a smaller collection frequency than
min_cfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded. min_df:int-
Added in version: 0.6.0
minimum document frequency of words. Words with a smaller document frequency than
min_dfare excluded from the model. The default value is 0, which means no words are excluded rm_top:int- the number of top words to be removed. If you want to remove too common words from model, you can set this value to 1 or more. The default value is 0, which means no top words are removed.
k:int- the number of topics between 1 ~ 32767.
vars:Iterable[str]-
indicating types of response variables. The length of
varsdetermines the number of response variables, and each element ofvarsdetermines a type of the variable. The list of available types is like below:- 'l': linear variable (any real value)
- 'b': binary variable (0 or 1)
alpha:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for document-topic
eta:float- hyperparameter of Dirichlet distribution for topic-word
mu:Union[float, Iterable[float]]- mean of regression coefficients
nu_sq:Union[float, Iterable[float]]- variance of regression coefficients
glm_param:Union[float, Iterable[float]]- the parameter for Generalized Linear Model
seed:int- random seed. The default value is a random number from
std::random_device{}in C++ corpus:Corpus-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a list of documents to be added into the model
transform:Callable[dict, dict]-
Added in version: 0.6.0
a callable object to manipulate arbitrary keyword arguments for a specific topic model
Ancestors
Instance variables
var f-
the number of response variables (read-only)
Methods
def add_doc(self, words, y=[])-
Add a new document into the model instance with response variables
yand return an index of the inserted document.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str y:Iterable[float]-
response variables of this document. The length of
ymust be equal to the number of response variables of the model (SLDAModel.f).Added in version: 0.5.1
If you have a missing value, you can set the item as
NaN. Documents withNaNvariables are included in modeling topics, but excluded from regression.
def estimate(self, doc)-
Return the estimated response variable for
doc. Ifdocis an unseen document instance which is generated bySLDAModel.make_doc()method, it should be inferred byLDAModel.infer()method first.Parameters
doc:Document- an instance of document or a list of them to be used for estimating response variables
def get_regression_coef(self, var_id)-
Return the regression coefficient of the response variable
var_id.Parameters
var_id:int- indicating the reponse variable, in range [0,
f)
def get_var_type(self, var_id)-
Return the type of the response variable
var_id. 'l' means linear variable, 'b' means binary variable. def make_doc(self, words, y=[])-
Return a new
Documentinstance for an unseen document withwordsand response variablesythat can be used forLDAModel.infer()method.Parameters
words:Iterable[str]- an iterable of
str y:Iterable[float]- response variables of this document.
The length of
ydoesn't have to be equal to the number of response variables of the model (SLDAModel.f). If the length ofyis shorter thanSLDAModel.f, missing values are automatically filled withNaN.
Inherited members
class TermWeight (value, names=None, *, module=None, qualname=None, type=None, start=1)-
This enumeration is for Term Weighting Scheme and it is based on following paper:
- Wilson, A. T., & Chew, P. A. (2010, June). Term weighting schemes for latent dirichlet allocation. In human language technologies: The 2010 annual conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 465-473). Association for Computational Linguistics.
There are three options for term weighting and the basic one is ONE. The others also can be applied for all topic models in
tomotopy.Expand source code
class TermWeight(IntEnum): """ This enumeration is for Term Weighting Scheme and it is based on following paper: > * Wilson, A. T., & Chew, P. A. (2010, June). Term weighting schemes for latent dirichlet allocation. In human language technologies: The 2010 annual conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 465-473). Association for Computational Linguistics. There are three options for term weighting and the basic one is ONE. The others also can be applied for all topic models in `tomotopy`. """ ONE = 0 """ Consider every term equal (default)""" IDF = 1 """ Use Inverse Document Frequency term weighting. Thus, a term occurring at almost every document has very low weighting and a term occurring at a few document has high weighting. """ PMI = 2 """ Use Pointwise Mutual Information term weighting. """Ancestors
- enum.IntEnum
- builtins.int
- enum.Enum
Class variables
var IDF-
Use Inverse Document Frequency term weighting.
Thus, a term occurring at almost every document has very low weighting and a term occurring at a few document has high weighting.
var ONE-
Consider every term equal (default)
var PMI-
Use Pointwise Mutual Information term weighting.